Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador (Spanish: República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"), is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. The territories of Ecuador include the Galápagos Islands (also known as Archipiélago de Colón) in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) west of the mainland. Total area of the country is 283,561 sq km, and the 2022 estimated population is 17,289,000. Mestizos account for 71.9% of Ecuador’s population (Mestizo is a term used for racial classification, which refers to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry). The capital is Quito. Below are: (1) a map of Ecuador showing its neighboring countries, and (2) a province map of Ecuador:

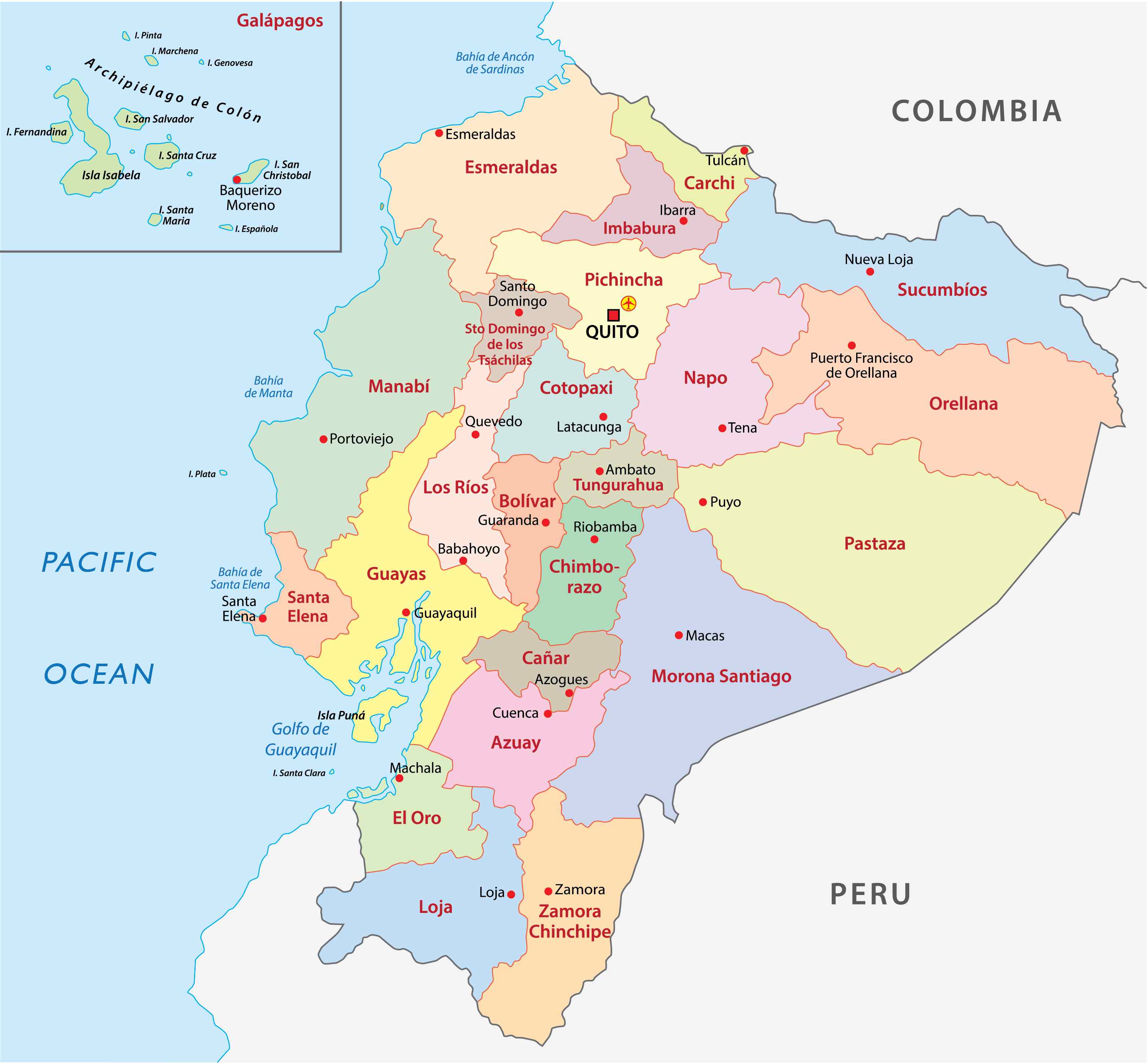
If you are interested, you can download a detailed map of Ecuador.
The state of Ecuador is a middle-income representative democratic republic and a developing country that is highly dependent on commodities, namely petroleum and agricultural products. It is governed as a democratic presidential republic.
The economy of Ecuador is the eighth largest in Latin America and the 69th largest in the world by total GDP (2020 ranking). Ecuador's economy is based on the export of oil, bananas, shrimp, and gold. It is the world's largest exporter of bananas ($3.38 billion in 2017) and a major exporter of shrimp ($3.06 billion in 2017). The country is substantially dependent on its petroleum resources. In 2017, oil accounted for about one-third of public-sector revenue and 32% of export earnings. Since 2000, Ecuador uses the U.S. dollar as official currency.
Ecuador has many volcanoes. They belong to the Northern Volcanic Zone of the Andes, which is the result of subduction of the Nazca Pacific oceanic plate under the continental plate of South America. The earliest report of a historical eruption was in 1628. More or less continuous eruptions were reported from 1728 until 1916, and again from 1934 to the present. One of Ecuador's most active volcanoes is Sangay, which is also one of the highest active volcanoes in the world. Located in the east of the Andean crest, with it's perfect steep cone shape and glacier-covered top, it towers majestically at 5,286 meters (17,343 feet) high above the Amazonian rainforest. The recent Sangay eruption began in March 2019 and has continued throughout 2021, which includes explosions with ash plumes, incandescent ejecta, lava flows, and lahars. Below is a webcam image on Oct. 18, 2021 captured a dense ash and steam plume rising 1,500 meter over the summit:

One of 17 megadiverse countries in the world, Ecuador hosts many endemic plants and animals, such as those of the Galápagos Islands. In recognition of its unique ecological heritage, the new constitution of 2008 is the first in the world to recognize legally enforceable Rights of Nature, or ecosystem rights.
Quito:
Quito, formally San Francisco de Quito, is the capital and most populous city of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its urban area. Quito is the capital city closest to the Equator, with its northern limits ending about 1 km (0.62 miles) south of the line. Below are” (1) a 1810 painting showing Spanish troops at the city of Quito, (2) a mid-19th century painting of Quito, and (3) street view of current Quito’s Old city leading up to the hill of El Panecillo with a view of the statue of the Virgin atop of the hill:



Quito is the political and cultural center of Ecuador. The country's major governmental, administrative, and cultural institutions are located within the city. The majority of transnational companies with a presence in Ecuador are headquartered there. It is also one of the country's two major industrial centers—the port city of Guayaquil being the other one.
Quito has the largest, least-altered, and best-preserved historic center in the Americas. This center was, together with the historic center of Kraków, Poland, the first to be declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO on 18 September 1978. The historic center of Quito is to the south of the capital's current center, on an area of 320 ha (790 acres), and one of the most important historic areas in Latin America. There are about 130 monumental buildings (which host a variety of pictorial art and sculpture, mostly religiously-inspired, in a multi-faceted range of schools and styles), and 5,000 properties registered in the municipal inventory of heritage properties.
Located 26 km (16 miles) north of the center of Quito is a tract of land called Ciudad Mitad del Mundo (Spanish for Middle of the World City). The grounds contain the Monument to the Equator, which highlights the exact location of the Equator (from which the country takes its name) and commemorates the eighteenth century Franco-Spanish Geodesic Mission which fixed its approximate location. Below are pictures of: (1) the Monument and (2) nearby areas.


Below are publications related to Ecuador:
(1) Ecuador's Constitution of 2008 with Amendments through 2015

(2) Ecuador (WTO 2020 Statistic)
(3) Primates of Ecuador (Ministry of Tourism, Ecuador)

(4) The Fiscal and Monetary History of Ecuador: 1950-2015

(5) Ecuador: An Overview (published 2021 by Congressional Research Service)

(6) Scientific Research in Ecuador: A Bibliometric Analysis

(7) Science Diplomacy in Ecuador: Political Discourse and Practices Between 2007 and 2017

(8) Ecuador - Assessment of Development Results

(9) Ecuador - Skills Matter: Additional Results from the Survey of Adult Skills

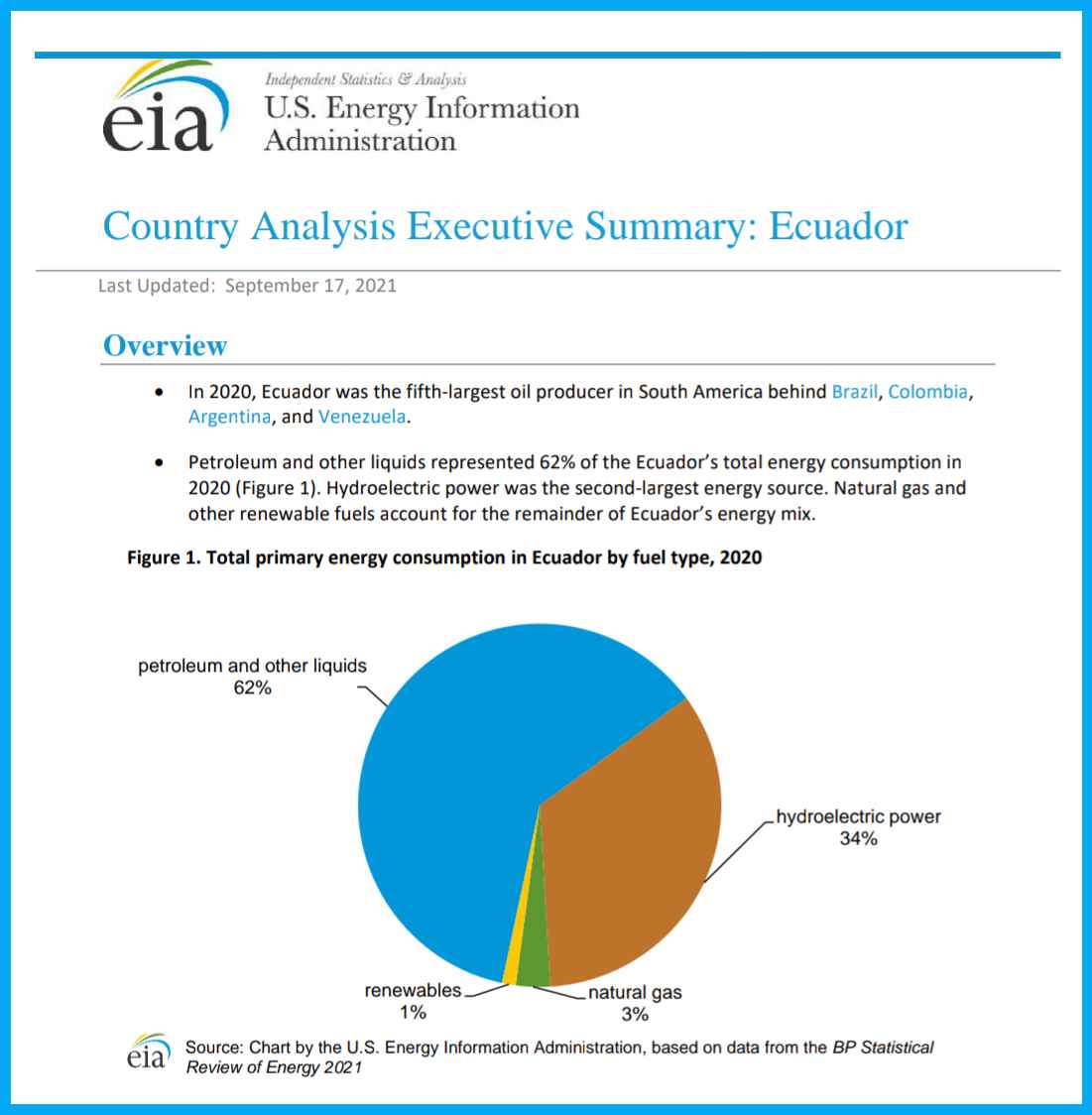
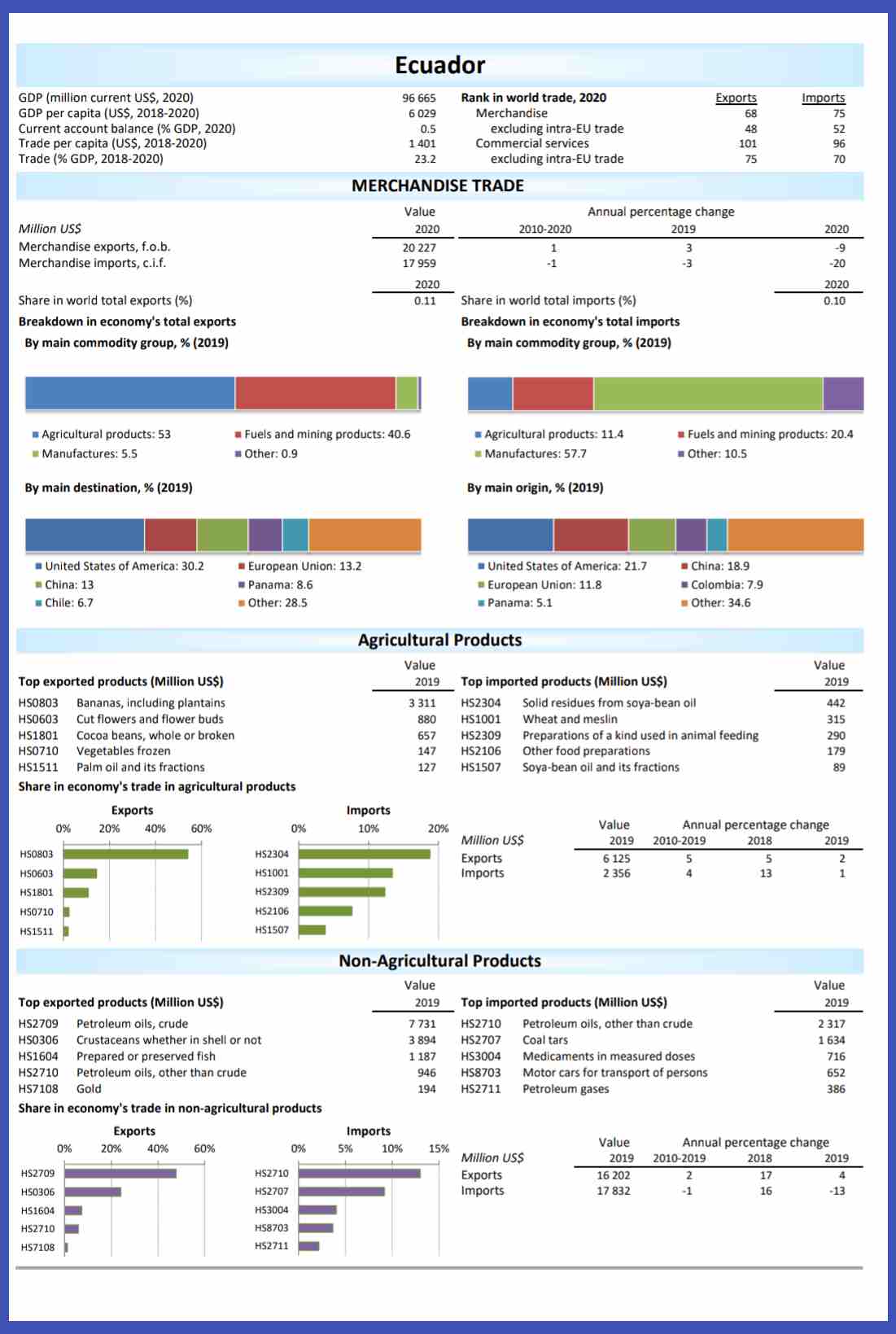
(10) Country Analysis Executive Summary: Ecuador (analysis of Ecuador's oil industry by U.S. Energy Information Administration, updated in 2021)